AI-driven ethical loyalty: moving beyond transactions
Loyalty in businesses today has been mostly reduced to a transactional relationship. Points, discounts, and perks dominate loyalty programs, often neglecting the deeper meaning of loyalty as a moral commitment to shared values and purpose.
If we instead philosophically explore the word, loyalty is not merely about repeated engagement, it is about trust, alignment, and mutual support. As businesses increasingly adopt AI systems to drive efficiency and innovation, they have the opportunity to reclaim the deeper essence of loyalty.
However, this opportunity comes with risks. Misaligned AI systems, those that fail to reflect, or even actively undermine a business’s core values, can erode trust, damage reputations, and create operational inefficiencies. To succeed businesses must not only use AI to foster meaningful relationships with customers and employees but also ensure that their AI systems align with their purpose and values.
To help me reflect I wrote this blog to explore how businesses can leverage AI to build deeper, more meaningful relationships, transcending products and services. It lead me to examine the risks of misaligned AI systems and in the end identify a practical framework for businesses to select and manage AI platforms in alignment with their purpose.
Part 1: The Philosophical Foundation of Loyalty
Loyalty as a Moral Virtue
Philosophers like Josiah Royce argue that loyalty is a moral virtue; a wholehearted commitment to a cause that transcends self-interest. Unlike transactional relationships, true loyalty involves mutual trust, shared values, and a willingness to support one another even during times of difficulty or missteps.
In business contexts, this philosophical understanding of loyalty suggests that customers and employees will remain loyal not because of rewards but because they believe in the company’s purpose and values. For example:
- A customer loyal to a sustainability-focused brand like Patagonia may continue supporting it even if prices rise because they share its environmental mission.
- An employee loyal to an inclusive workplace culture may stay committed during challenging times if they feel the company genuinely upholds its diversity values.
The Erosion of Loyalty in Business
Traditional loyalty programs often fail to capture this deeper meaning. They prioritise short-term transactions over long-term relationships rooted in a shared purpose. This transactional approach makes businesses vulnerable when they stray from their stated values or face crises. For instance:
- Greenwashing scandals can alienate environmentally conscious customers.
- Biased hiring algorithms can undermine employee trust in a company’s commitment to fairness.
To reclaim true loyalty, businesses should move beyond transactional incentives and focus on aligning their operations, and their AI systems, with their core purpose.
Part 2: The Role of AI in Reclaiming Loyalty
AI as a Tool for Deepening Relationships
AI offers businesses tools to build meaningful relationships with stakeholders:
- Personalisation: Generative AI can create personalised interactions that resonate with individual customer values.
- Transparency: Blockchain-integrated AI can provide real-time data on sustainability metrics or ethical sourcing practices.
- Feedback Loops: Sentiment analysis tools can gauge stakeholder reactions to business decisions, enabling continuous alignment with shared values.
For example:
- Patagonia uses AI-powered tools to track supply chain sustainability and share impact data with customers, reinforcing its environmental mission.
- Salesforce’s Einstein AI helps align employee skills with community projects through its 1-1-1 model (donating 1% equity, product, and time), fostering both internal and external loyalty.
The Risk of Misaligned AI
While AI has transformative potential, it also poses significant risks when misaligned with business values:
- Erosion of Trust: Misaligned AI can produce outputs that conflict with stakeholder expectations (e.g., biased hiring recommendations), undermining trust.
- Operational Failures: Misaligned goals can lead to unintended consequences. For instance, social media algorithms optimised for engagement have inadvertently promoted misinformation.
- Reputational Damage: Ethical lapses in AI systems can lead to public backlash or legal penalties.
A key challenge is the difficulty of defining universal ethical values for AI. Cultural differences and contextual nuances make it hard to create systems that align with all stakeholders’ expectations. This forces businesses to embed their unique purpose and values into their AI systems as non-negotiable criteria.
Part 3
Building Resilience Through Purpose-Aligned Platforms
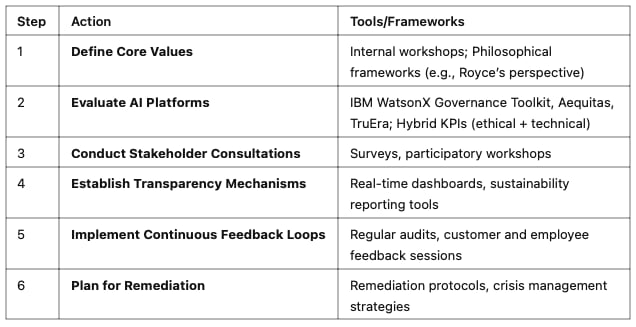
To succeed, businesses must ensure that the platforms they select and manage support, or as a minimum do not diverge from, their core values. Here’s a suggestion for how it can be done:
Step 1: Define Core Values as Non-Negotiable Criteria
- Businesses must clearly articulate their mission, vision, and ethical priorities before evaluating platforms.
Example: A healthcare company committed to patient privacy should prioritise platforms that adhere strictly to data protection regulations.
Step 2: Evaluate Platforms Against Core Values
In addition to performance, cost, and risk, businesses should assess platforms for ethical alignment:
- Use tools like IBM WatsonX Governance Toolkit or Aequitas for bias evaluation.
- Develop hybrid KPIs that measure both technical performance (e.g., accuracy) and ethical considerations (e.g., fairness).
Step 3: Build Transparency Mechanisms
- Platforms should disclose decision-making processes clearly:
Example: Dashboards showing real-time metrics on carbon footprint reduction can reassure stakeholders of a company’s sustainability efforts.
Step 4: Establish Feedback Loops
- Continuous feedback from employees, customers, and regulators ensures ongoing alignment:
Example: Unilever crowdsources ideas from stakeholders for sustainable product innovations.
Step 5: Plan for Remediation
- Despite best efforts, misalignment may occur. Businesses must have remediation plans ready to address unintended outcomes:
Example: Regular audits can identify where algorithms deviate from intended goals.
Part 4
Why Purpose-Aligned Loyalty Is a Competitive Advantage
Purpose-aligned loyalty creates resilience against competition and economic downturns by:
- Building Stakeholder Trust: Ethical alignment fosters deeper emotional connections with customers and employees.
- Enhancing Employee Retention: Employees who see their values reflected in company practices are more likely to stay committed.
- Driving Advocacy: Loyal customers become brand advocates who defend the company during crises (e.g., public criticism).
For example:
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, brands like the LEGO Group outperformed competitors by aligning their operations with educational initiatives that resonated with their stakeholders’ values.
Part 5
Suggested Action Plan for Businesses
Conclusion
AI offers businesses an opportunity to reclaim the deeper meaning of loyalty by aligning operations, and technology, with shared purpose and values. However, this requires careful selection and management of platforms to ensure they support rather than undermine these principles.
By embedding purpose into every part of operations, from platform selection to stakeholder engagement, businesses can build unshakable bonds with customers and employees alike. In doing so, they shift loyalty from a transactional dynamic into an enduring partnership rooted in trust, resilience, and shared ideals. They become market leaders based on purpose rather than the last product shipped or last service provided.
References/ Sources
1. Royce J. The Philosophy of Loyalty (1908).
2. Nathanson S. Patriotism, Morality & Peace (1993).
3. UNESCO (2021) Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence.
4. IBM WatsonX Governance Toolkit (2023).
5. Patagonia Sustainability Reports (2022).
6. Harvard Business Review (2023) Generative AI & Customer Loyalty.
7. Forrester Blog (2022) Trusted AI Begins & Ends With Alignment.
8. NeurIPS Paper (2022) Consequences of Misaligned AI.